Zeno's paradoxes
Zeno's paradoxes are a set of problems generally thought to have been devised by Zeno of Elea to support Parmenides's doctrine that "all is one" and that, contrary to the evidence of our senses, the belief in plurality and change is mistaken, and in particular that motion is nothing but an illusion. It is usually assumed, based on Plato's Parmenides 128c-d, that Zeno took on the project of creating these paradoxes because other philosophers had created paradoxes against Parmenides's view. Thus Zeno can be interpreted as saying that to assume there is plurality is even more absurd than assuming there is only "the One" (Parmenides 128d). Plato makes Socrates claim that Zeno and Parmenides were essentially arguing exactly the same point (Parmenides 128a-b).
Several of Zeno's nine surviving paradoxes (preserved in Aristotle's Physics[1] and Simplicius's commentary thereon) are essentially equivalent to one another; and most of them were regarded, even in ancient times, as very easy to refute.[1] Three of the strongest and most famous—that of Achilles and the tortoise, the Dichotomy argument, and that of an arrow in flight—are presented in detail below.
Zeno's arguments are perhaps the first examples of a method of proof called reductio ad absurdum also known as proof by contradiction. They are also credited as a source of the dialectic method used by Socrates.[2]
While more modern calculus has solved the mathematical aspects of the paradox,[3] Zeno's paradoxes remain a problem for philosophers.[4][5][6] Variations on the paradoxes (see Thomson's lamp) continue to produce philosophical problems.
The origins of the paradoxes are somewhat unclear. Diogenes Laertius, citing Favorinus, says that Zeno's teacher Parmenides, was the first to introduce the Achilles and the Tortoise Argument. But in a later passage, Laertius attributes the origin of the paradox to Zeno, explaining that Favorinus disagrees.[7]
Contents |
The Paradoxes of Motion
Achilles and the tortoise
| “ | In a race, the quickest runner can never overtake the slowest, since the pursuer must first reach the point whence the pursued started, so that the slower must always hold a lead. | ” |
|
—Aristotle, Physics VI:9, 239b15 |
||
In the paradox of Achilles and the Tortoise, Achilles is in a footrace with the tortoise. Achilles allows the tortoise a head start of 100 metres. If we suppose that each racer starts running at some constant speed (one very fast and one very slow), then after some finite time, Achilles will have run 100 metres, bringing him to the tortoise's starting point. During this time, the tortoise has run a much shorter distance, say, 10 metres. It will then take Achilles some further time to run that distance, by which time the tortoise will have advanced farther; and then more time still to reach this third point, while the tortoise moves ahead. Thus, whenever Achilles reaches somewhere the tortoise has been, he still has farther to go. Therefore, because there are an infinite number of points Achilles must reach where the tortoise has already been, he can never overtake the tortoise.[8][9]
The dichotomy paradox
| “ | That which is in locomotion must arrive at the half-way stage before it arrives at the goal. | ” |
|
—Aristotle, Physics VI:9, 239b10 |
||
Suppose Homer wants to catch a stationary bus. Before he can get there, he must get halfway there. Before he can get halfway there, he must get a quarter of the way there. Before traveling a fourth, he must travel one-eighth; before an eighth, one-sixteenth; and so on.
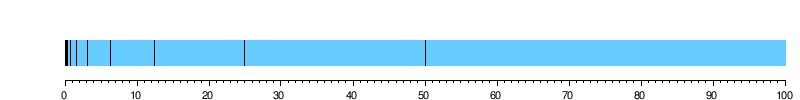
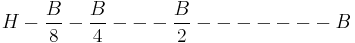
The resulting sequence can be represented as:
This description requires one to complete an infinite number of tasks, which Zeno maintains is an impossibility.
This sequence also presents a second problem in that it contains no first distance to run, for any possible (finite) first distance could be divided in half, and hence would not be first after all. Hence, the trip cannot even begin. The paradoxical conclusion then would be that travel over any finite distance can neither be completed nor begun, and so all motion must be an illusion.
This argument is called the Dichotomy because it involves repeatedly splitting a distance into two parts. It contains some of the same elements as the Achilles and the Tortoise paradox, but with a more apparent conclusion of motionlessness. It is also known as the Race Course paradox. Some, like Aristotle, regard the Dichotomy as really just another version of Achilles and the Tortoise.[10]
The arrow paradox
| “ | If everything when it occupies an equal space is at rest, and if that which is in locomotion is always occupying such a space at any moment, the flying arrow is therefore motionless. | ” |
|
—Aristotle, Physics VI:9, 239b5 |
||
In the arrow paradox (also known as the fletcher's paradox), Zeno states that for motion to occur, an object must change the position which it occupies. He gives an example of an arrow in flight. He states that in any one instant of time, for the arrow to be moving it must either move to where it is, or it must move to where it is not. However, it cannot move to where it is not, because this is a single instant, and it cannot move to where it is because it is already there. In other words, in any instant of time there is no motion occurring, because an instant is a snapshot. Therefore, if it cannot move in a single instant it cannot move in any instant, making any motion impossible.
Whereas the first two paradoxes presented divide space, this paradox starts by dividing time—and not into segments, but into points.[11]
Three other paradoxes as given by Aristotle
Paradox of Place:
- "… if everything that exists has a place, place too will have a place, and so on ad infinitum."[12]
Paradox of the Grain of Millet:
- "… there is no part of the millet that does not make a sound: for there is no reason why any such part should not in any length of time fail to move the air that the whole bushel moves in falling. In fact it does not of itself move even such a quantity of the air as it would move if this part were by itself: for no part even exists otherwise than potentially."[13]
The Moving Rows:
- "The fourth argument is that concerning the two rows of bodies, each row being composed of an equal number of bodies of equal size, passing each other on a race-course as they proceed with equal velocity in opposite directions, the one row originally occupying the space between the goal and the middle point of the course and the other that between the middle point and the starting-post. This...involves the conclusion that half a given time is equal to double that time."[14]
For an expanded account of Zeno's arguments as presented by Aristotle, see Simplicius' commentary On Aristotle's Physics.
Proposed solutions
Aristotle (384 BC−322 BC) remarked that as the distance decreases, the time needed to cover those distances also decreases, so that the time needed also becomes increasingly small.[15] Aristotle's proposed solution for the paradoxes involves distinguishing "things infinite in respect of divisibility" (such as a unit of space that can be mentally divided into ever smaller units while remaining spatially the same) from things (or distances) that are infinite in extension ("with respect to their extremities").[16]
Before 212 BC, Archimedes had developed a method to derive a finite answer for the sum of infinitely many terms that get progressively smaller. (See: Geometric series, 1/4 + 1/16 + 1/64 + 1/256 + · · ·, The Quadrature of the Parabola.) Modern calculus achieves the same result, using more rigorous methods (see convergent series, where the "reciprocals of powers of 2" series, equivalent to the Dichotomy Paradox, is listed as convergent). These methods allow construction of solutions stating that under suitable conditions (i.e. the distances are progressively geometrically decreasing), the travel time is finite (bounded by a fixed upper bound).[3][17]
Saint Thomas Aquinas offered the following solution to the arrow paradox: "Instants are not parts of time, for time is not made up of instants any more than a magnitude is made of points, as we have already proved. Hence it does not follow that a thing is not in motion in a given time, just because it is not in motion in any instant of that time." [18]
Peter Lynds has taken this idea further, arguing that all of Zeno's motion paradoxes are resolved by the conclusion that instants in time and instantaneous magnitudes do not actually exist.[19] Lynds argues that an object in relative motion cannot have a determined relative position (for if it did, it could not be in motion), and so cannot have its motion fractionally dissected as though it does as in the paradoxes.
Another proposed solution[3][20] is to question the assumption inherent in Zeno's paradox, which is that between any two different points in space (or time), there is always another point. Without this assumption there are only a finite number of distances between two points, hence there is no infinite sequence of movements, and the paradox is resolved.
Reichenbach has proposed that the paradox may arise from considering space and time as separate entities. In a theory like general relativity, which presumes a single space-time continuum, the paradox may be blocked.[21]
The paradoxes in modern times
Infinite processes remained theoretically troublesome in mathematics until the late 19th century. The epsilon-delta version of Weierstrass and Cauchy developed a rigorous formulation of the logic and calculus involved. These works resolved the mathematics involving infinite processes.[22]
While mathematics can be used to calculate where and when the moving Achilles will overtake the Tortoise of Zeno's paradox, philosophers such as Brown and Moorcroft[4][5] claim that mathematics does not address the central point in Zeno's argument, and that solving the mathematical issues does not solve every issue the paradoxes raise.
Zeno's arguments are often misrepresented in the popular literature. That is, Zeno is often said to have argued that the sum of an infinite number of terms must itself be infinite - that both the distance and the time to be travelled are infinite. However, Zeno's problem was not with finding the sum of an infinite sequence, but rather with finishing an infinite number of tasks: how can one ever get from A to B, if an infinite number of events can be identified that need to precede the arrival at B, and one cannot reach even the beginning of a "last event"?[4][5][6][23]
Today there is still a debate on the question of whether or not Zeno's paradoxes have been resolved. In The History of Mathematics, Burton writes, "Although Zeno's argument confounded his contemporaries, a satisfactory explanation incorporates a now-familiar idea, the notion of a 'convergent infinite series.'"[24] Bertrand Russell offered a "solution" to the paradoxes based on modern physics, but Brown concludes "Given the history of 'final resolutions', from Aristotle onwards, it's probably foolhardy to think we've reached the end. It may be that Zeno's arguments on motion, because of their simplicity and universality, will always serve as a kind of 'Rorschach image' onto which people can project their most fundamental phenomenological concerns (if they have any)."[4]
The quantum Zeno effect
In 1977,[25] physicists E. C. G. Sudarshan and B. Misra studying quantum mechanics discovered that the dynamical evolution (motion) of a quantum system can be hindered (or even inhibited) through observation of the system.[26] This effect is usually called the "quantum Zeno effect" as it is strongly reminiscent of Zeno's arrow paradox.
This effect was first theorized in 1958.[27]
Zeno behavior
In the field of verification and design of timed and hybrid systems, the system behaviour is called Zeno if it includes an infinite number of discrete steps in a finite amount of time.[28] Some formal verification techniques exclude these behaviours from analysis, if they are not equivalent to non-Zeno behaviour.[29][30] In systems design these behaviours will also often be excluded from system models, since they cannot be implemented with a digital controller.[31] A simple example of a system showing Zeno behavior is the model of a bouncing ball.
Writings about Zeno’s paradoxes
Zeno’s paradoxes have inspired many writers
- Leo Tolstoy in War and Peace (Part 11,Chapter I) discusses the race of Achilles and the tortoise when critiquing "historical science".
- In the dialogue What the Tortoise Said to Achilles, Lewis Carroll describes what happens at the end of the race. The tortoise discusses with Achilles a simple deductive argument. Achilles fails in demonstrating the argument because the tortoise leads him into an infinite regression.
- In Gödel, Escher, Bach by Douglas Hofstadter, the various chapters are separated by dialogues between Achilles and the tortoise, inspired by Lewis Carroll’s works
- The Argentinian writer Jorge Luis Borges discusses Zeno’s paradoxes many times in his work, showing their relationship with infinity. Borges also used Zeno’s paradoxes as a metaphor for some situations described by Kafka. Jorge Luis Borges traces, in an essay entitled "Avatars of the Tortoise", the many recurrences of this paradox in works of philosophy. The successive references he traces are Agrippa the Skeptic, Thomas Aquinas, Hermann Lotze, F.H. Bradley and William James.[32]
See also
|
|
|
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Aristotle's Physics "Physics" by Aristotle translated by R. P. Hardie and R. K. Gaye
- ↑ ([fragment 65], Diogenes Laertius. IX 25ff and VIII 57)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Boyer, Carl (1959). The History of the Calculus and Its Conceptual Development. Dover Publications. p. 295. ISBN 9780486605098. http://books.google.com/?id=w3xKLt_da2UC&dq=zeno+calculus&q=zeno#v=snippet&q=zeno. Retrieved 26 February 2010. ""If the paradoxes are thus stated in the precise mathematical terminology of continuous variables (...) the seeming contradictions resolve themselves.""
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Brown, Kevin. "Zeno and the Paradox of Motion". Reflections on Relativity. http://www.mathpages.com/rr/s3-07/3-07.htm. Retrieved 6 June 2010.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Moorcroft, Francis. "Zeno's Paradox". http://www.philosophers.co.uk/cafe/paradox5.htm.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Papa-Grimaldi, Alba (1996). "Why Mathematical Solutions of Zeno's Paradoxes Miss the Point: Zeno's One and Many Relation and Parmenides' Prohibition". The Review of Metaphysics. http://www.webalice.it/keithalba/timeandreality/zeno_revmet.htm.
- ↑ Diogenes Laertius, Lives, 9.23 and 9.29.
- ↑ "Math Forum". http://mathforum.org/isaac/problems/zeno1.html., matchforum.org
- ↑ Huggett, Nick (2004). "Zeno's Paradoxes: 3.2 Achilles and the Tortoise". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/paradox-zeno/#AchTor. Retrieved 2009-11-18
- ↑ Huggett, Nick (2004). "Zeno's Paradoxes: 3.1 The Dichotomy". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/paradox-zeno/#Dic. Retrieved 2009-11-18
- ↑ Huggett, Nick (2004). "Zeno's Paradoxes: 3.3 The Arrow". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/paradox-zeno/#Arr. Retrieved 2009-11-18
- ↑ Aristotle Physics IV:1, 209a25
- ↑ Aristotle Physics VII:5, 250a20
- ↑ Aristotle Physics VI:9, 239b33
- ↑ Aristotle. Physics 6.9
- ↑ Aristotle. Physics 6.9; 6.2, 233a21-31
- ↑ George B. Thomas, Calculus and Analytic Geometry, Addison Wesley, 1951
- ↑ Aquinas. Commentary on Aristotle's Physics, Book 6.861
- ↑ Lynds, Peter. Time and Classical and Quantum Mechanics: Indeterminacy vs. Discontinuity. Foundations of Physics Letters (Vol. 16, Issue 4, 2003). doi:10.1023/A:1025361725408
- ↑ van Bendegem, Jean Paul (1987). "Discussion:Zeno's Paradoxes and the Tile Argument". Philosophy of Science (Belgium) 54: 295–302. doi:10.1086/289379. http://www.jstor.org/pss/187807. Retrieved 2010-02-27.
- ↑ Hans Reichenbach (1958) The Philosophy of Space and Time. Dover
- ↑ Lee, Harold (1965). "Are Zeno's Paradoxes Based on a Mistake?". Mind (Oxford University Press) 74 (296): 563–570. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2251675. Retrieved 24 February 2010.
- ↑ Huggett, Nick (2004). "Zeno's Paradoxes: 5. Zeno's Influence on Philosophy". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/paradox-zeno/#ZenInf. Retrieved 2009-11-18
- ↑ Burton, David, A History of Mathematics: An Introduction, McGraw Hill, 2010, ISBN 978-0073383156
- ↑ Sudarshan, E. C. G.; Misra, B. (1977). "The Zeno’s paradox in quantum theory". Journal of Mathematical Physics 18 (4): 756–763. doi:10.1063/1.523304. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1977JMP....18..756M
- ↑ W.M.Itano; D.J.Heinsen, J.J.Bokkinger, D.J.Wineland (1990). "Quantum Zeno effect" (PDF). PRA 41: 2295–2300. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.41.2295. http://www.boulder.nist.gov/timefreq/general/pdf/858.pdf.
- ↑ Khalfin, L.A. (1958). Soviet Phys. JETP 6: 1053
- ↑ Paul A. Fishwick, ed (1 June 2007). "15.6 "Pathological Behavior Classes" in chapter 15 "Hybrid Dynamic Systems: Modeling and Execution" by Pieter J. Mosterman, The Mathworks, Inc.". Handbook of dynamic system modeling. Chapman & Hall/CRC Computer and Information Science (hardcover ed.). Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press. pp. 15–22 to 15–23. ISBN 9781584885658. http://books.google.com/?id=cM-eFv1m3BoC&pg=SA15-PA22. Retrieved 5 March 2010.
- ↑ Lamport, Leslie (2002) (PDF). Specifying Systems. Addison-Wesley. p. 128. ISBN 0-321-14306-X. http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/lamport/tla/book-02-08-08.pdf. Retrieved 6 March 2010.
- ↑ Zhang, Jun; Johansson, Karl; Lygeros, John; Sastry, Shankar (2001). "Zeno hybrid systems". International Journal for Robust and Nonlinear control. http://aphrodite.s3.kth.se/~kallej/papers/zeno_ijnrc01.pdf. Retrieved 2010-02-28.
- ↑ Franck, Cassez; Henzinger, Thomas; Raskin, Jean-Francois (2002). A Comparison of Control Problems for Timed and Hybrid Systems. http://mtc.epfl.ch/~tah/Publications/a_comparison_of_control_problems_for_timed_and_hybrid_systems.html. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ↑ Borges, Jorge Luis (1964). Labyrinths. London: Penguin. pp. 237–243.
References
- Kirk, G. S., J. E. Raven, M. Schofield (1984) The Presocratic Philosophers: A Critical History with a Selection of Texts, 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521274559.
- Huggett, Nick (2004). "Zeno's Paradoxes". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/paradox-zeno/. Retrieved 2009-11-18.
- Plato (1926) Plato: Cratylus. Parmenides. Greater Hippias. Lesser Hippias, H. N. Fowler (Translator), Loeb Classical Library. ISBN 0674991850.
- Sainsbury, R.M. (2003) Paradoxes, 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521483476.
External links
- Silagadze, Z . K. "Zeno meets modern science,"
- Platonic Realms: "Zeno's Paradox of the Tortoise and Achilles."
- Zeno's Paradox: Achilles and the Tortoise by Jon McLoone, Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- Zeno's Paradoxes, by Bradley Dowden, 2009, Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
This article incorporates material from Zeno's paradox on PlanetMath, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.
